Social Self-Efficacy and Internet Gaming Disorder Among Chinese Undergraduates: The Mediating Role of Alexithymia and the Moderating Role of Empathy
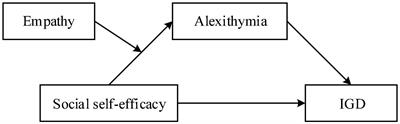
As an increasingly serious social problem, Internet gaming disorder (IGD) of college students may be related to their social self-efficacy. However, the relationship and its internal mechanisms underlying are still unclear. The current study tested the mediating effect of alexithymia in the associat…
- Zhang, Y., Liang, T., Gan, X., Zheng, X., Li, H., & Zhang, J. (2022). Social Self-Efficacy and Internet Gaming Disorder Among Chinese Undergraduates: The Mediating Role of Alexithymia and the Moderating Role of Empathy. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 898554. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.898554
社会問題として深刻化する大学生のインターネットゲーム障害(IGD)は、大学生の社会的自己効力感と関連している可能性がある。しかし、その関係や内部メカニズムはまだ不明である。本研究では、社会的自己効力感とIGDの関連におけるアレキシサイミアの媒介効果、およびこの媒介過程が共感によって調整されるかどうかを検証した。中国人大学生888名を対象に、社会的自己効力感尺度(PSSE)、中国版インターネットゲーム嗜癖尺度(IGAS-C)、トロント・アレキシサイミア尺度(TAS-20)、対人反応尺度(IRI-C)を採用しモデルを検討した。その結果、社会的自己効力感は、IGDと有意に負の相関を示した。また、調停分析により、アレキシサイミアは社会的自己効力感とIGDとの関連を媒介することが示された。さらに、モデレート媒介分析により、媒介効果は共感度が低いほど強いことが明らかとなった。この結論は、アレキシサイミアは社会的自己効力感とIGDの関連を媒介し、その媒介効果は共感を介して調整されるというメカニズムを裏付け、明らかにするものである。また、これらの知見は、大学が教育活動を行う際の参考となると同時に、学部生のIGDを予防するための科学的な示唆を与えている。
