Social Bullying Among Undergraduates: The Roles of Internet Gaming Disorder, Risk-Taking Behavior, and Internet Addiction
An issue that affects the academic engagement, performance, health and wellbeing of university undergraduates is bullying. Substantial literature has examined the predictors of bullying perpetration, but there is little research on the contributions of internet-related factors and the propensity to…
- Nwanosike, C. L., Ujoatuonu, I. V. N., Kanu, G. C., Ike, O. O., & Okeke, T. J. (2022). Social Bullying Among Undergraduates: The Roles of Internet Gaming Disorder, Risk-Taking Behavior, and Internet Addiction. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 830794. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.830794
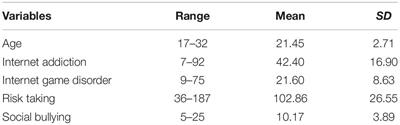
大学学部生の学業への取り組み、成績、健康、ウェルビーイングに影響を与える問題にいじめがある。いじめ加害の予測因子については実質的な文献が検討されているが、いじめにおけるインターネット関連因子とリスクテイク傾向の寄与についてはほとんど研究がない。我々は、社会的いじめにおけるIGD、リスクテイク行動、インターネット嗜癖の役割について検討した。データ収集には、以下の4つの尺度を用いた。データ収集には、Young Adult Social Behavior Scale(YASB)、Internet Gaming Disorder Scale(IGDS9-SF)、Domain-Specific Risk-Taking Scale、Internet Addiction Test(IAT)Scaleの4種類の尺度を使用した。参加者はナイジェリア大学Nsukka校の学部生552名で、男性143名、女性409名(年齢幅=17〜32歳、M=21.45、SD=2.71)である。回帰分析の結果、ゲーム障害(GD)およびリスクテイク行動は、社会的いじめと正の相関があることが示された。したがって、インターネットゲームに嗜癖し、リスクをとるほど、いじめに発展する可能性が高い。インターネット嗜癖は、社会的いじめとは有意な関連を示さなかった。いじめの加害性を抑制するためには、学部生の機能不全的なインターネット利用、GD、リスクテイク行動の割合を最小限に抑える努力が必要である。
